.png)
Breaking Ground: Biodegradable Building Innovations
In today's rapidly evolving world, the need for sustainable building materials and technologies has become more pressing than ever before. As we face environmental challenges such as climate change and resource depletion, the construction industry is increasingly turning to biodegradable and innovative solutions to create more eco-friendly buildings.
In this article, we will explore the exciting advancements in biodegradable building materials and technologies, examining their potential to revolutionize the way we design and construct our built environment. From bioplastics to green concrete, these innovative solutions offer not only environmental benefits but also economic advantages and improved performance.
Join us as we delve into the world of biodegradable and innovative building materials and technologies, discovering how they are shaping the future of sustainable architecture and construction. Together, we can pave the way towards a greener, more sustainable future for generations to come.
Biodegradable materials are revolutionizing the construction industry by offering sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials. These materials are designed to break down naturally over time, reducing environmental impact and promoting circularity in the construction process.
One of the most promising biodegradable materials is bioplastic, which is derived from renewable sources such as corn starch or sugarcane. Bioplastics can be used in various construction applications, including insulation, roofing, and even structural components. Unlike traditional plastics, which can take hundreds of years to decompose, bioplastics biodegrade much faster, making them an eco-friendly choice for building materials.
Another innovative biodegradable material is mycelium-based composite, which is made from the roots of mushrooms. Mycelium has the remarkable ability to bind together organic matter, creating a durable and lightweight material that can be molded into various shapes. Mycelium-based composites are being explored for use in insulation, packaging, and even furniture, offering a biodegradable alternative to conventional materials like polystyrene.
Additionally, biodegradable concrete is gaining traction as a sustainable building material. This eco-friendly concrete incorporates recycled aggregates and bio-based additives, reducing its carbon footprint and enhancing its environmental performance. Biodegradable concrete can be used in a wide range of construction applications, from sidewalks and pavements to structural elements like beams and columns.
Overall, biodegradable materials offer a promising solution to the environmental challenges facing the construction industry. By exploring and adopting these innovative materials, architects and builders can create more sustainable buildings that minimize waste, conserve resources, and contribute to a healthier planet.
Innovative building technologies are reshaping the construction industry, offering new solutions to age-old challenges and driving sustainable practices. These technologies leverage advancements in materials science, digital design, and automation to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance the performance of buildings.
One such technology is 3D printing, which allows for the rapid fabrication of complex architectural elements using a layer-by-layer deposition process. This method enables architects to create intricate designs with greater precision and customization while minimizing material waste. 3D printing is being used to produce everything from building components to entire structures, revolutionizing the way buildings are constructed.
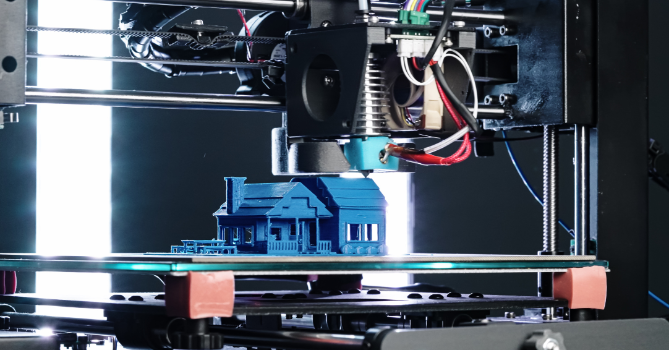
Another innovative technology is Building Information Modeling (BIM), which enables architects and engineers to create detailed digital models of buildings and infrastructure. BIM allows for better collaboration, visualization, and analysis throughout the design and construction process, leading to more efficient workflows and improved project outcomes. By simulating different design scenarios and optimizing building performance, BIM helps architects make informed decisions that enhance sustainability and resilience.
Additionally, smart building technologies are transforming the way buildings are operated and maintained. These technologies integrate sensors, actuators, and data analytics to monitor and control various building systems, such as lighting, HVAC, and security. By optimizing energy usage, improving occupant comfort, and predicting maintenance needs, smart building technologies help reduce operational costs and environmental impact while enhancing the user experience.
Furthermore, modular construction techniques are gaining popularity for their efficiency and flexibility. Modular construction involves prefabricating building components off-site and assembling them on-site, reducing construction time, labor costs, and material waste. This approach allows for greater standardization and quality control while enabling architects to design buildings that are adaptable to changing needs and environments.
Overall, innovative building technologies hold tremendous potential to revolutionize the construction industry and promote sustainability. By embracing these technologies, architects can create buildings that are not only functional and aesthetically pleasing but also environmentally responsible and resilient to future challenges.
Vernacular architecture refers to the traditional building practices that have evolved over time in response to local environmental conditions, cultural influences, and available materials. This approach emphasizes sustainability by utilizing locally sourced materials, passive design strategies, and indigenous building techniques to create structures that harmonize with their surroundings and minimize environmental impact.
One key aspect of vernacular architecture is its reliance on biodegradable and renewable materials, such as wood, mud, thatch, and stone, which are abundant and readily available in the local environment. By using these materials, vernacular buildings reduce the need for energy-intensive manufacturing processes and transportation, thus lowering their carbon footprint.
Additionally, vernacular architecture often incorporates passive design principles to optimize thermal comfort and energy efficiency. Features such as thick walls, small windows, and natural ventilation systems help regulate indoor temperatures and reduce the need for mechanical heating and cooling. This not only decreases energy consumption but also enhances the resilience of buildings to extreme weather conditions.
Moreover, vernacular architecture fosters a deeper connection between people and their built environment, preserving cultural heritage and promoting community cohesion. By drawing inspiration from local traditions and adapting to regional climates and landscapes, vernacular buildings reflect the wisdom of generations past and offer valuable lessons for sustainable design practices today.
In conclusion, vernacular architecture exemplifies the principles of sustainability by harnessing local resources, embracing passive design strategies, and fostering a sense of place and identity. By learning from vernacular traditions and integrating them into contemporary architectural practices, designers can create buildings that are not only environmentally responsible but also culturally enriching and socially inclusive.
While biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies offer promising solutions for sustainable construction, they also present unique challenges and opportunities that must be addressed to realize their full potential.
One of the main challenges is the scalability and affordability of biodegradable materials. While these materials are often environmentally friendly and renewable, they may be more expensive or less readily available than conventional building materials. Additionally, their performance characteristics and durability may vary, requiring thorough testing and certification to ensure compliance with building codes and standards.

Another challenge is the need for technological innovation and research to advance biodegradable materials and building technologies. This includes developing new manufacturing processes, improving material properties, and optimizing construction techniques to enhance their performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, there are logistical challenges associated with sourcing and transporting biodegradable materials, especially in regions where they are not locally available. This may require establishing new supply chains, investing in infrastructure, and overcoming regulatory barriers to facilitate their widespread adoption.
Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities associated with biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies. For example, they offer architects and designers greater flexibility and creativity in their projects, allowing them to explore new aesthetic possibilities and design solutions that integrate seamlessly with the natural environment.
Moreover, biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies can contribute to a more circular economy by reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental impact throughout the building lifecycle. By embracing these opportunities and overcoming challenges, the construction industry can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient built environment.
Examining real-world applications of biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies provides valuable insights into their effectiveness, feasibility, and potential impact on sustainable construction practices.
One notable case study is the G.T. Mickey Leland Federal Building in Houston, Texas, designed by Gensler. This project utilized sustainable design principles and biodegradable materials to achieve LEED Platinum certification, the highest standard for green building. The building features energy-efficient systems, water-saving measures, and biodegradable materials such as reclaimed wood, recycled steel, and low-VOC paints. These sustainable features not only reduce the building's environmental footprint but also create a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment for occupants.
In the United Kingdom, noteworthy vernacular buildings demonstrate the long-standing tradition of sustainable architecture. These buildings, such as thatched cottages and cob houses, are constructed using locally sourced, natural materials like timber, straw, and earth. They showcase the effectiveness of vernacular building techniques in achieving thermal comfort, structural integrity, and aesthetic appeal while minimizing environmental impact. By studying these vernacular buildings, architects and designers can draw inspiration from time-tested methods of sustainable construction and apply them to modern building projects.
Similarly, in Scotland, vernacular buildings exhibit a strong connection to the natural environment and local craftsmanship. From traditional stone cottages to turf-roofed houses, these buildings showcase the resilience and adaptability of vernacular architecture in diverse climatic conditions. By incorporating sustainable materials and building techniques inspired by vernacular traditions, architects and builders can create environmentally friendly and culturally sensitive structures that reflect the unique identity of their surroundings.
These case studies highlight the diverse applications of biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies in real-world projects, demonstrating their potential to revolutionize the construction industry and pave the way for a greener future. By learning from these examples and embracing sustainable design principles, architects and builders can contribute to the global effort to mitigate climate change and promote environmental stewardship.
Looking ahead, the future of biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies holds promising opportunities for advancing sustainability in the construction industry.
One emerging trend is the integration of bioplastics into building materials, offering a renewable and biodegradable alternative to traditional plastics. These bioplastics, derived from plant-based sources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, can be used to create durable and eco-friendly products like insulation panels, roofing materials, and façade claddings. As technology continues to improve, bioplastics are expected to become more cost-effective and widely adopted in construction projects, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and landfill waste.
Another promising trend is the development of smart building systems that optimize energy efficiency and resource utilization. These systems utilize sensors, automation, and data analytics to monitor and control building operations in real-time, maximizing energy savings, and minimizing environmental impact. By incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines, smart buildings can further enhance their sustainability performance and resilience to climate change.
Furthermore, the rise of prefabrication and modular construction techniques is expected to revolutionize the way buildings are designed and built. Prefabricated components made from biodegradable materials can streamline construction processes, reduce waste, and lower construction costs. Additionally, modular construction allows for greater flexibility and scalability, enabling rapid deployment of sustainable housing solutions in response to changing environmental and social needs.
Overall, the future of biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies holds immense potential for driving sustainable development and resilience in the built environment. By embracing these trends and leveraging technology to advance sustainability goals, the construction industry can play a pivotal role in creating a greener, more resilient future for generations to come.
In conclusion, the exploration of biodegradable materials and innovative building technologies offers a glimpse into a more sustainable future for the construction industry. With the increasing focus on environmental conservation and the need to mitigate the impacts of climate change, these advancements present viable solutions to address the challenges faced by the built environment.
By embracing biodegradable materials and leveraging innovative technologies, such as smart building systems and modular construction techniques, we can build structures that are not only environmentally friendly but also more resilient, efficient, and cost-effective. The integration of vernacular architecture principles further enhances sustainability by drawing inspiration from traditional building practices that prioritize harmony with nature and local resource utilization.
As we navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by sustainable construction, it is essential to continue investing in research, development, and collaboration to drive progress towards a more sustainable and resilient built environment for future generations.