BidLight Model Health
The Model Health feature is designed to provide users with a comprehensive view of the health status of their 3D models. This feature ensures that models adhere to predefined rules and standards, enabling users to identify and address issues that may affect the integrity, performance, or compliance of the model.
Key Components
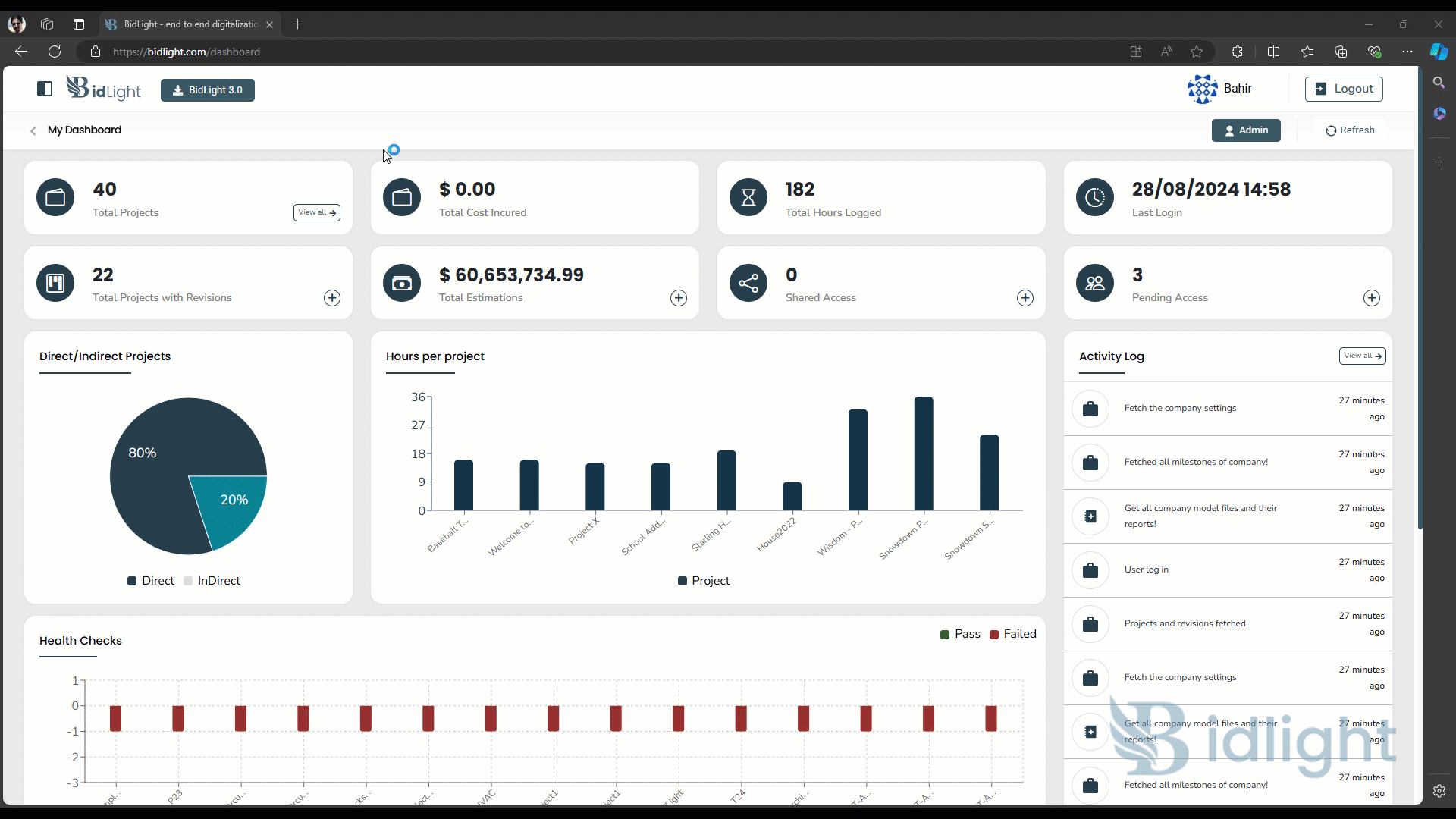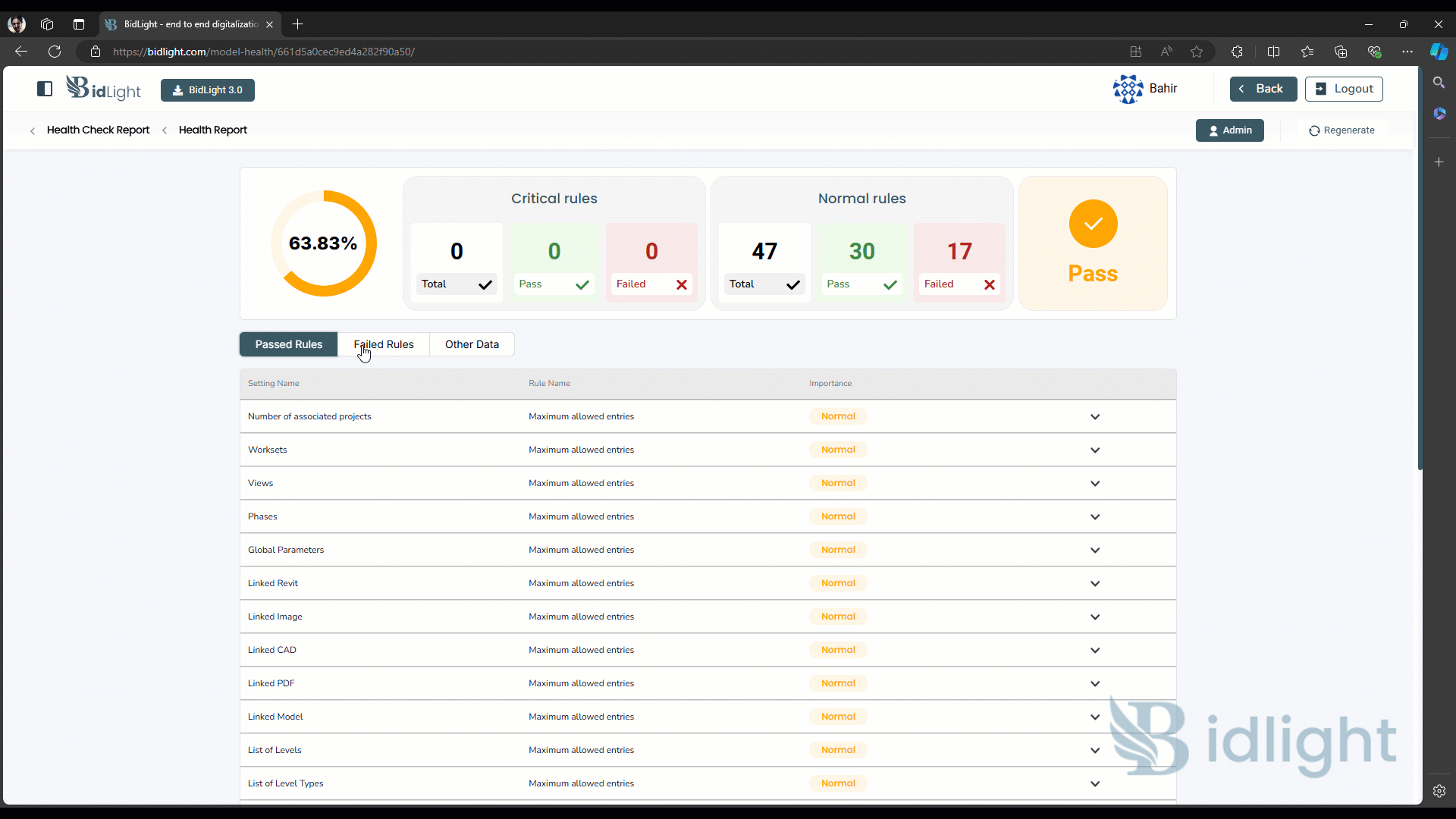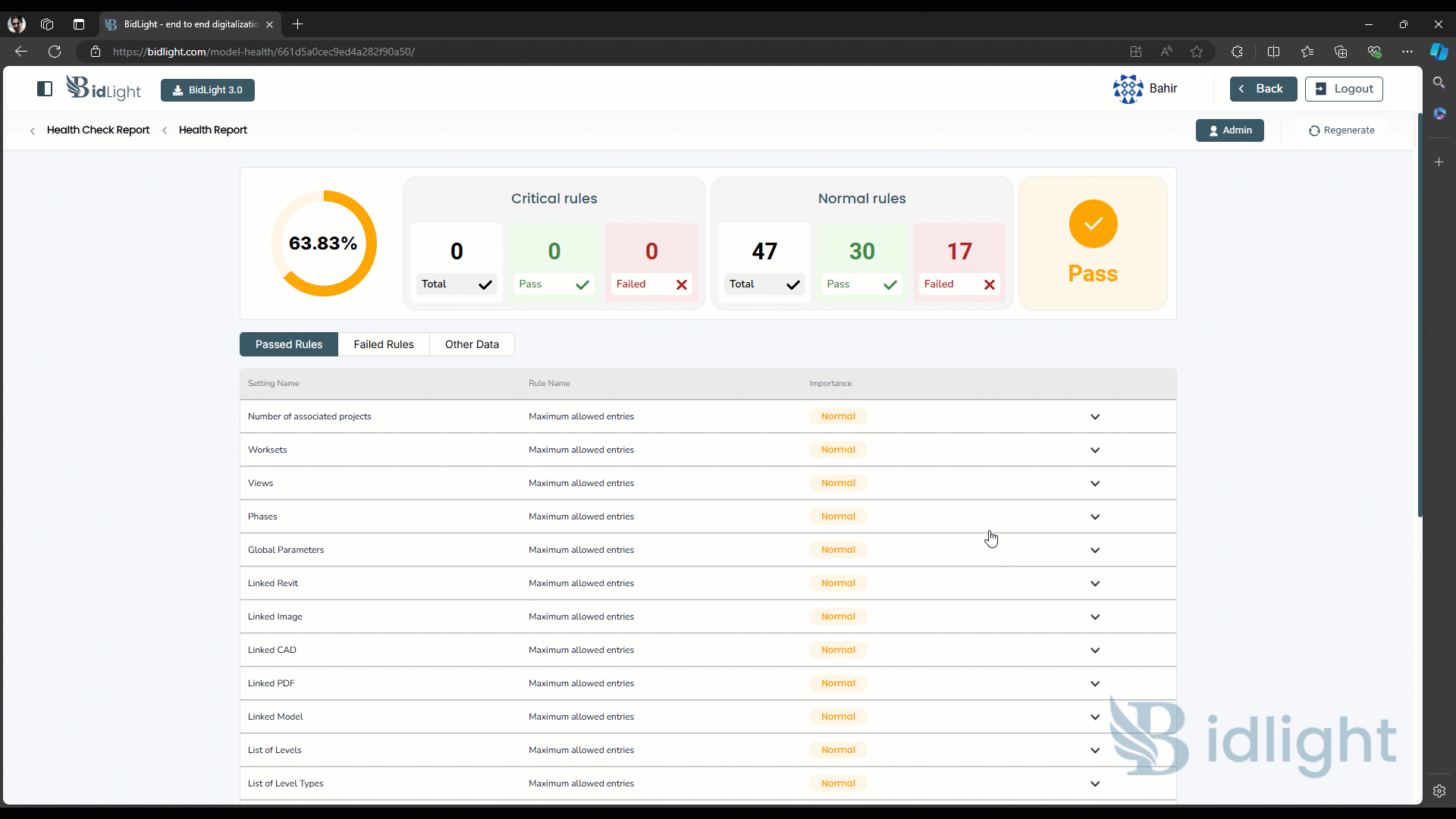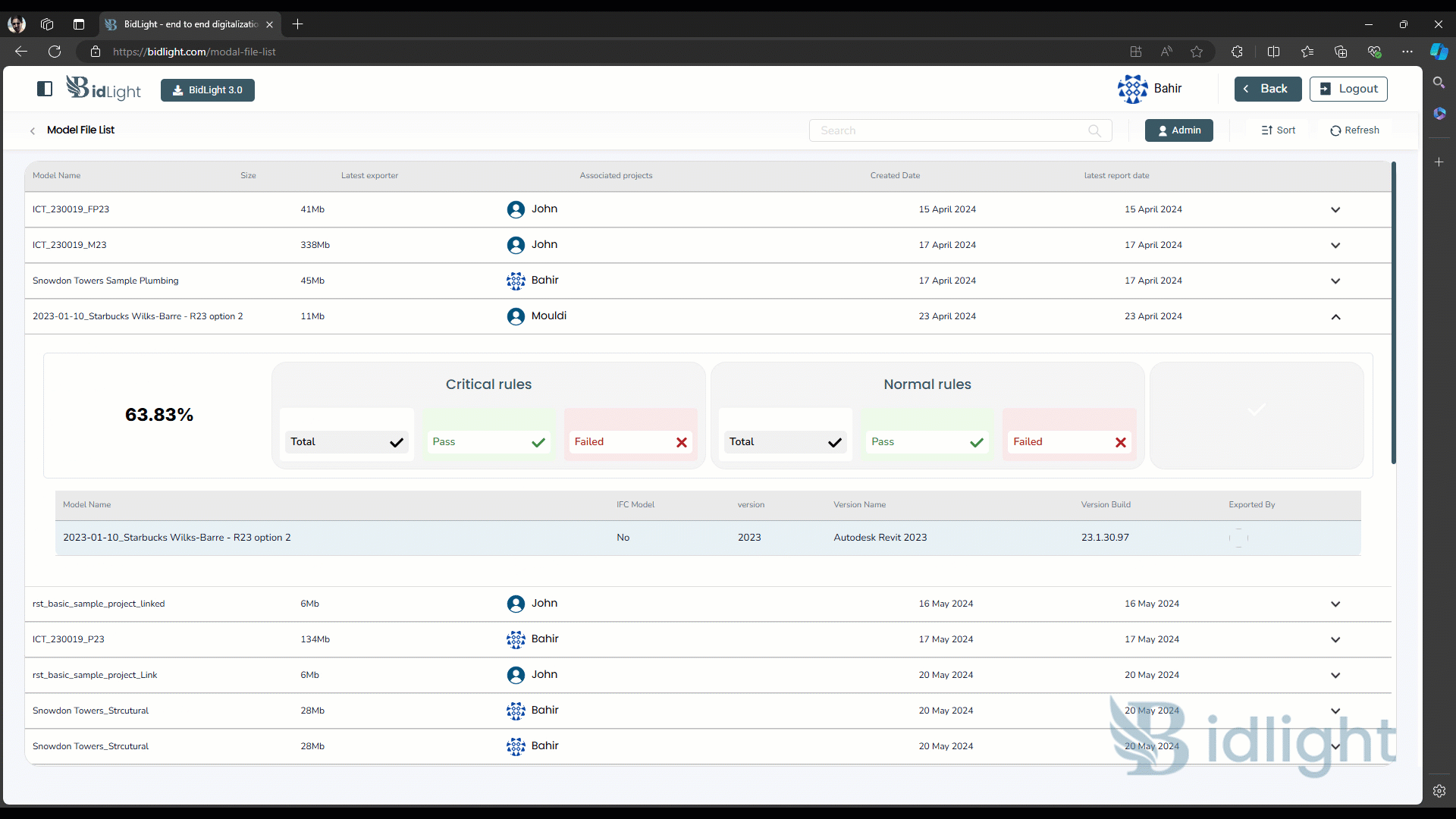
- Detailed Model Report:
○ Passed Rules: The report includes a section that lists all the rules that the model has passed. This ensures that the model meets the necessary criteria for quality, compliance, and performance.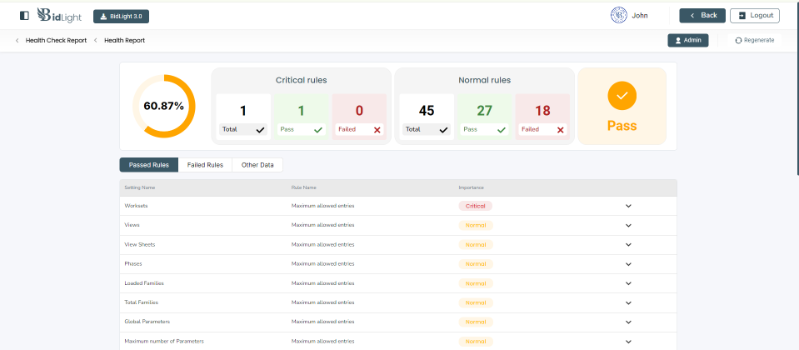
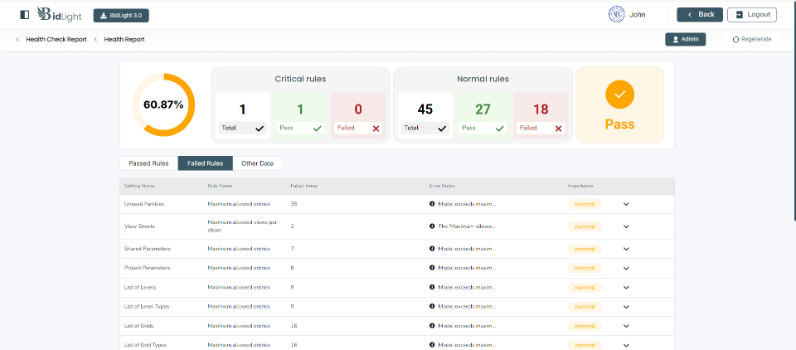
○ Failed Rules: The report highlights any rules that the model has failed to meet. This is crucial for identifying areas that require attention or correction. Each failed rule is accompanied by detailed information, including the nature of the failure and potential impacts on the model.
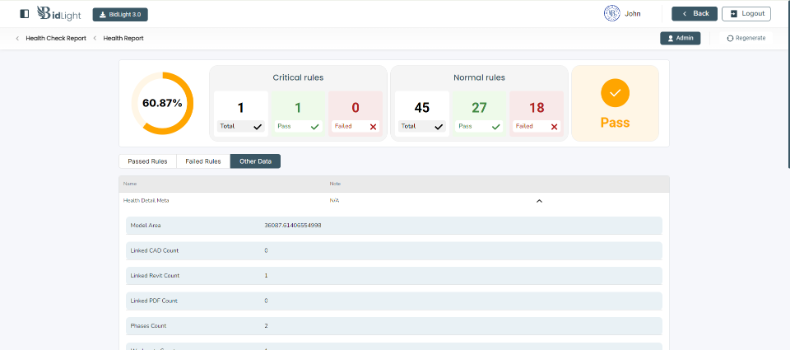
○ Other Rules: In addition to passed and failed rules, the report also includes a section for other rules that are relevant but may not directly impact the model's current state. This could include rules that are not applicable or optional, providing users with a full spectrum view of model health.
2. Model Health Dashboard:
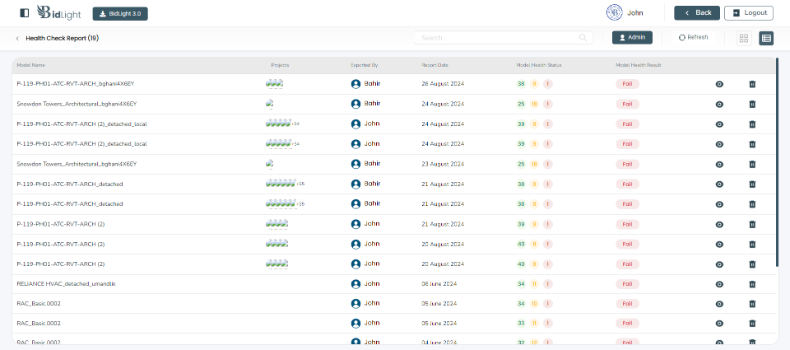
i. Viewing Health Reports: Users can view a list of all health reports associated with a model. The dashboard provides quick access to each report, allowing users to drill down into specific details as needed. Reports are typically listed with key metadata, such as the date of the report, the overall health score, and the number of passed and failed rules.
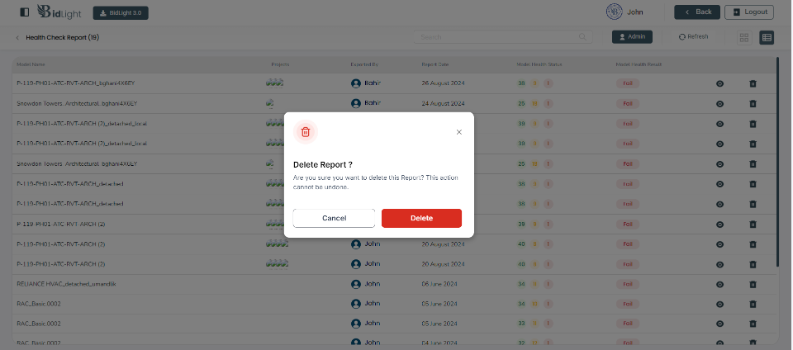
ii. Deleting Health Reports: Users have the option to delete old or irrelevant health reports. This helps in keeping the workspace organized and ensures that only the most relevant data is retained. Deletion is typically accompanied by a confirmation prompt to prevent accidental loss of important reports.
3. User Interactions
● Accessing Reports: Users can access model health reports directly from the model health dashboard. The interface is designed for ease of use, with clear navigation to switch between different models and their associated reports.
● Interpreting Data: The report includes visual aids, such as charts and graphs, to help users quickly interpret the health status of their models. These visuals highlight key metrics like the percentage of rules passed, the severity of failures, and trends over time.
● Actions Based on Reports: Users can take actions based on the health reports, such as initiating corrective workflows for failed rules or sharing reports with team members for collaborative review.
4. Benefits
● Improved Model Quality: By providing detailed insights into the health of models, this feature helps users maintain high standards of quality and compliance, reducing the risk of errors or issues downstream.
● Efficient Issue Resolution: The clear identification of failed rules allows users to quickly address and rectify issues, improving overall productivity and reducing downtime.
● Organized Workspace: The ability to view and delete reports ensures that users can maintain an organized workspace, focusing only on relevant data and actions.
Conclusion
The Model Health feature is an essential tool for ensuring the integrity and quality of 3D models within the system. With detailed reporting on passed, failed, and other rules, coupled with user-friendly tools for managing and interacting with these reports, this feature significantly enhances the user's ability to maintain and improve model standards.